Sound wave theory 09
Why do sound waves lose energy and diminish?
- Video
- Script
Welcome to this tutorial on why sound waves loses energy and diminish.
As it travels, a sound wave's energy is slowly lost as heat. This happens because the molecules of the medium through which it is travelling knock against each other as they transmit the sound wave energy.
Because a gas, such as the air, presents less friction to a sound wave than a solid, it can travel a longer distance before all it's energy is lost. A solid barrier such as a wall, on the other hand, will quickly absorb the sound wave, and prevent it from travelling as far.
Caption - Speed and absorption
Although sound travels faster through solids than gases, it's energy is more quickly absorbed and it will either emerge on the other side quieter or duller or not at all.
Caption - The effect of frequency
The rate at which a soundwave is absorbed by a barrier depends on it's frequency. Taking the example of a simple sine wave, if the barrier is wider than the wavelength, the wave will be absorbed.
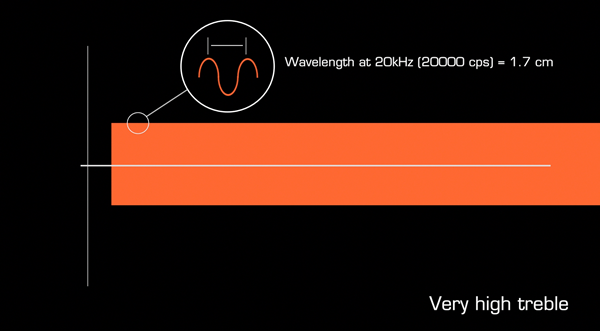
A sine wave at 20kHz has a wavelength of 1.7 cm , so is easily absorbed by most barriers.
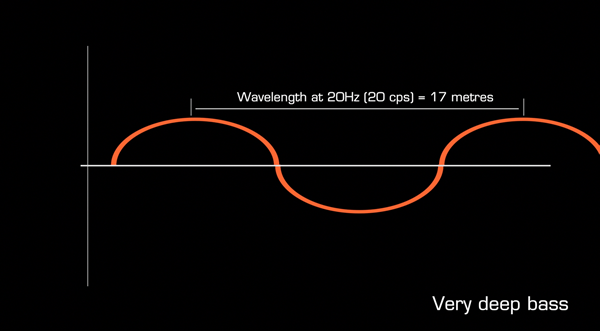
A sine wave at 20Hz has a wavelength of 17 meters and will therefore pass through most barriers.
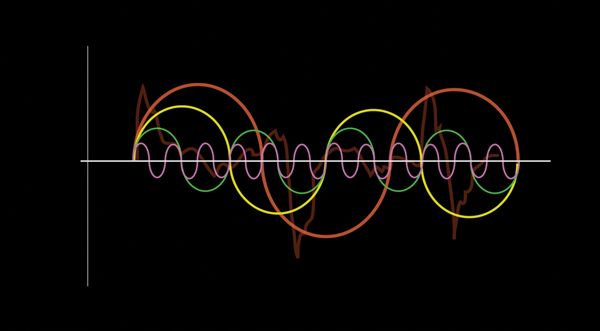
Caption - Absorption of harmonics
If a soundwave contains multiple harmonics at a wide range of frequencies, such as in a completed mix, not all of those harmonics will be absorbed at the same rate. Higher frequencies, with their shorter wavelengths, are absorbed faster than lower frequencies. This explains why we hear only the lower mid and bass frequencies of a completed mix through a barrier such as a wall.
Caption - Attenuation and absorption coefficients
Attenuation and absorption coefficients rate how well materials stop and deflect sound waves. The are used by recording studio architects to specify materials that will disperse sound and sound proof a room. The attenuation co-efficient expresses the overall level of sound energy loss from absorption and deflection.
Search online for "Absorption Coefficients of Building Materials" to find the absorption properties of different materials.
Caption - Thanks for watching
The script for this video, with accompanying images, can be found at projectstudiohandbook.com
We suggest you subscribe at our YouTube channel, and join our mailing list at our website to receive notification of new videos, blog posts and subscriber only extras.
Thanks for watching.